Middleware
- Introduction
- Lifecycle
- Received Middleware
- Captured Middleware
- Matching Middleware
- Heard Middleware
- Sending Middleware
- Example
Introduction
BotMan comes with a thorough middleware system, which is flexible and powerful. It allows you to hook custom integration logic into multiple parts of the chatbot lifecycle, such as receiving messages, matching message patterns and sending messages back to the user. Every available middleware comes with an interface that your middleware class can implement, so you can compose your own middleware classes, the way you need them.
Lifecycle
This chart shows you the lifecycle of the incoming chatbot requests and each steps they go through:
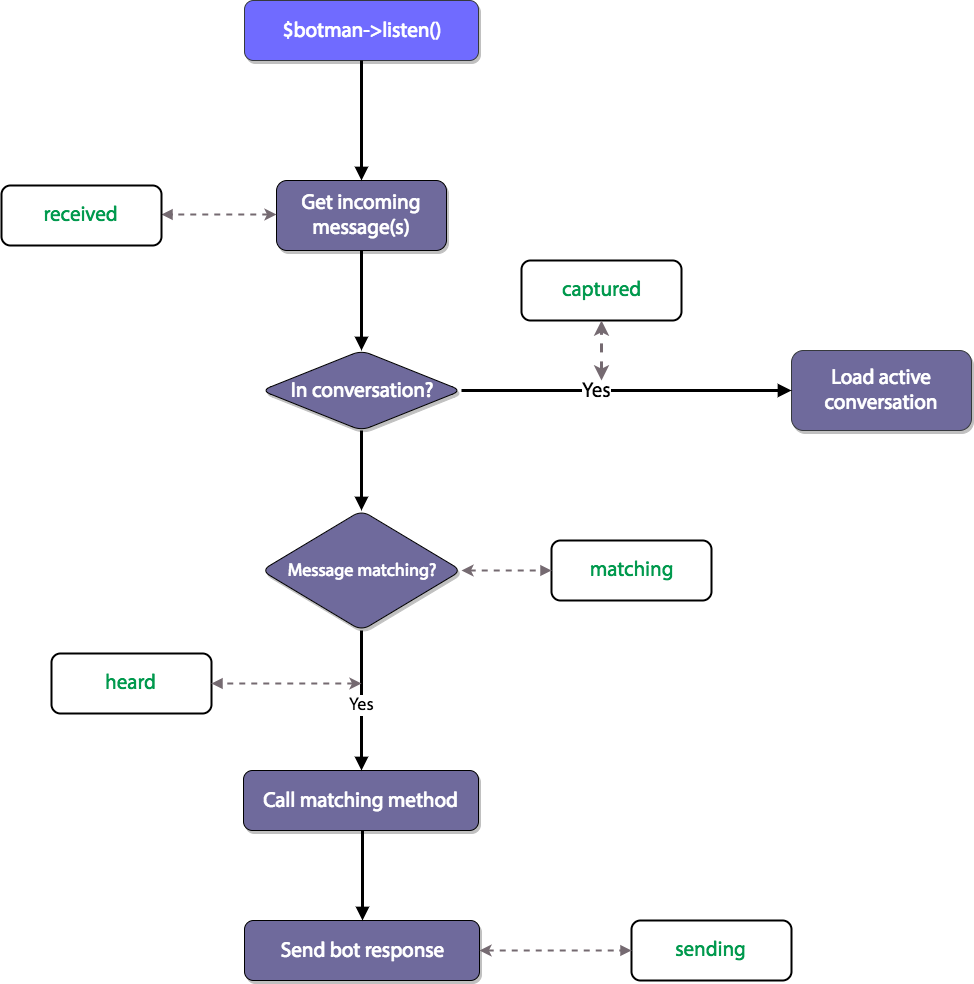
Received Middleware
The received middleware can be used to manipulate all incoming messaging service requests. This can for example be used to pre-process the incoming data and send it to a natural language processing tool, such as API.ai or RASA NLU. Since the received middleware needs to be applied to all incoming requests, it needs to be defined globally.
Example middleware class
This example received middleware takes the incoming message and adds some extra information to it, which can be used later throughout your chatbot application.
As multiple middleware classes can be applied, make sure to return a call to $next with the incoming message as a parameter.
use BotMan\BotMan\Interfaces\Middleware\Received;
class CustomReceivedMiddleware implements Received
{
/**
* Handle an incoming message.
*
* @param IncomingMessage $message
* @param callable $next
* @param BotMan $bot
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function received(IncomingMessage $message, $next, BotMan $bot)
{
$message->addExtras('custom_message_information', 'my custom value');
return $next($message);
}
}
Applying the middleware
To apply your custom received middleware, you may simply add it to the middleware stack using the $botman->middleware->received method.
Make sure to call this method before you call the listen() method, as the middleware won't be loaded otherwise.
$middleware = new CustomReceivedMiddleware();
$botman->middleware->received($middleware);
Captured Middleware
The captured middleware processes incoming answers when the current user is inside a conversation flow. This middleware will only be executed when your user is currently in a conversation and gives an answer to one of your conversation questions.
Since the captured middleware needs to be applied to all incoming requests, it needs to be defined globally.
Example middleware class
This example captured middleware takes the incoming message and adds some extra information to it, which can be used later throughout your chatbot application.
As multiple middleware classes can be applied, make sure to return a call to $next with the incoming message as a parameter.
use BotMan\BotMan\Interfaces\Middleware\Captured;
class CustomCapturedMiddleware implements Captured
{
/**
* Handle a captured message.
*
* @param IncomingMessage $message
* @param callable $next
* @param BotMan $bot
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function captured(IncomingMessage $message, $next, BotMan $bot)
{
$message->addExtras('custom_message_information', 'my custom value');
return $next($message);
}
}
Applying the middleware
To apply your custom captured middleware, you may simply add it to the middleware stack using the $botman->middleware->captured method.
Make sure to call this method before you call the listen() method, as the middleware won't be loaded otherwise.
$middleware = new CustomCapturedMiddleware();
$botman->middleware->captured($middleware);
Matching Middleware
The matching middleware defines how the messages will be matched. It receives the result of the regular expression check and can perform additional checks too. This method is useful when testing incoming messages against natural language processing results - such as intents. This middleware can be applied per message that should be heard from BotMan.
Example middleware class
This example matching middleware takes the incoming message and checks not only for the regular expression match - but also checks that the message was sent from a specific user. Every BotMan commands under this middleware will only be heard, when the correct pattern is sent and the correct user sends the message. Otherwise BotMan will not call the command callback.
use BotMan\BotMan\Interfaces\Middleware\Matching;
class CustomMatchingMiddleware implements Matching
{
/**
* @param IncomingMessage $message
* @param string $pattern
* @param bool $regexMatched Indicator if the regular expression was matched too
* @return bool
*/
public function matching(IncomingMessage $message, $pattern, $regexMatched)
{
return $regexMatched && $message->getSender() === 'Administrator';
}
}
Applying the middleware
To apply your custom matching middleware, you may either group multiple commands to use this middleware using the group method, or only apply the middleware to specific commands using the middleware method. Unless the other middlewares available, the matching middleware is not applied globally, but on a per command level.
$middleware = new CustomMatchingMiddleware();
// Let single command use this matching middleware
$botman->hears('keyword', function ($bot) {
//
})->middleware($middleware);
// Let multiple commands use this matching middleware
$botman->group(['middleware' => $middleware], function ($botman) {
$botman->hears('command one', function ($bot) { });
$botman->hears('command two', function ($bot) { });
});
Heard Middleware
The heard middleware works similar to how the received middleware works. It also processes the incoming message, but unlike the received middleware, the heard middleware will only be executed when the message was actually matched.
Example middleware class
This example heard middleware takes the incoming message and adds some extra information to it, which can be used later throughout your chatbot application.
As multiple middleware classes can be applied, make sure to return a call to $next with the incoming message as a parameter.
use BotMan\BotMan\Interfaces\Middleware\Heard;
class CustomHeardMiddleware implements Heard
{
/**
* Handle a message that was successfully heard, but not processed yet.
*
* @param IncomingMessage $message
* @param callable $next
* @param BotMan $bot
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function heard(IncomingMessage $message, $next, BotMan $bot)
{
$message->addExtras('custom_message_information', 'my custom value');
return $next($message);
}
}
Applying the middleware
To apply your custom heard middleware, you may simply add it to the middleware stack using the $botman->middleware->heard method.
Make sure to call this method before you call the listen() method, as the middleware won't be loaded otherwise.
$middleware = new CustomHeardMiddleware();
$botman->middleware->heard($middleware);
Sending Middleware
The sending middleware gets called before each message is sent out to the recipient. You can use this middleware to process outgoing messages and track every message that you send, for example using an analytics service.
You can also manipulate the outgoing payload data before it gets sent to the messaging service.
Example middleware class
This example sending middleware simply logs the outgoing payload data into a file called log.txt.
use BotMan\BotMan\Interfaces\Middleware\Sending;
class CustomCapturedMiddleware implements Sending
{
/**
* Handle an outgoing message payload before/after it
* hits the message service.
*
* @param mixed $payload
* @param callable $next
* @param BotMan $bot
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function sending($payload, $next, BotMan $bot)
{
file_put_contents('log.txt', print_r($payload, true));
return $next($payload);
}
}
Applying the middleware
To apply your custom sending middleware, you may simply add it to the middleware stack using the $botman->middleware->sending method.
Make sure to call this method before you call the listen() method, as the middleware won't be loaded otherwise.
$middleware = new CustomSendingMiddleware();
$botman->middleware->sending($middleware);